The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a type of tax on the consumption of goods and services in countries, collected by businesses from consumers and paid to the government.It was introduced officially in India on 1 July 2017, replacing the earlier system of multiple taxes, such as excise duty, service tax, and value-added tax (VAT).
The 101st Constitutional Amendment / One Hundred and First Amendment Act, 2016 of the Constitution of India is a significant piece of legislation that has had a prominent impact on the Indian economy. It was passed in 2016 to introduce the Goods and Services Tax (GST), a value-added tax (VAT) that has simplified the tax system and boosted economic growth. This constitutional amendment was introduced as a nationwide Goods and Services Tax (GST) concept in India.
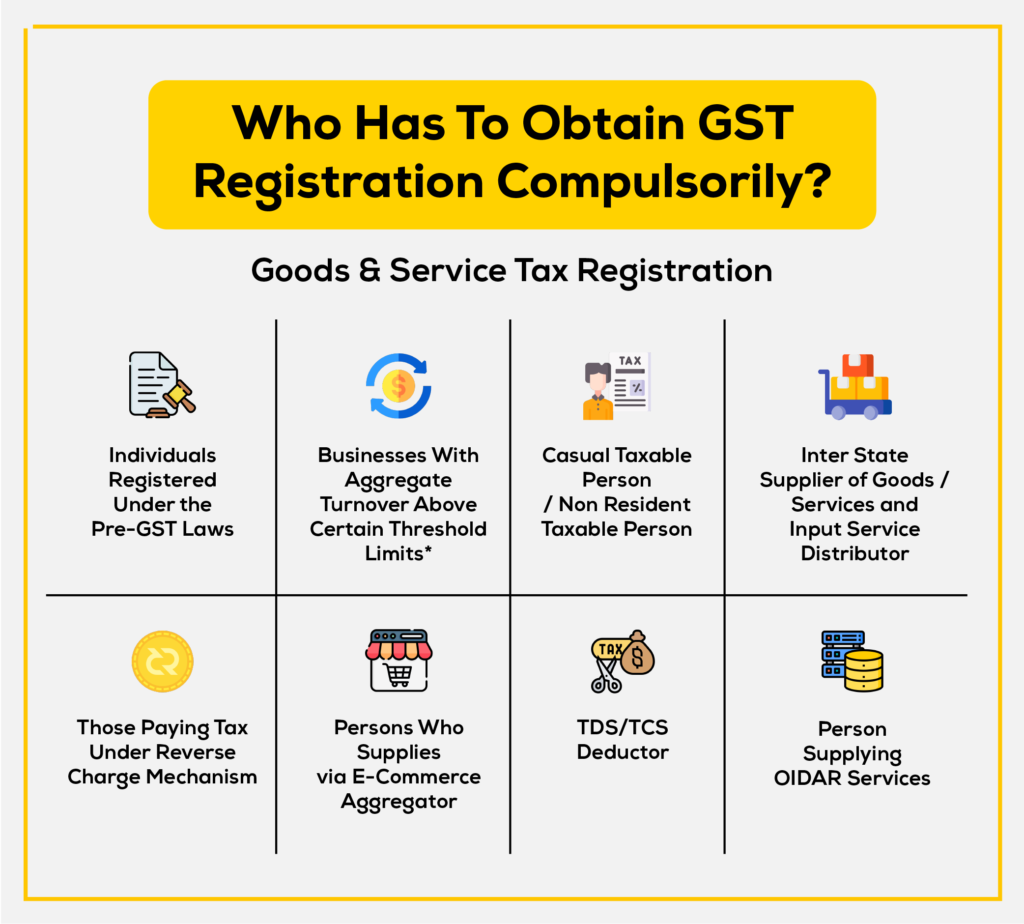
GST registration is mandatory for all businesses with an annual turnover of more than ₹40 lakhs (₹ 20 lakhs for businesses in special category states).
Note: Know about GST registration in a clear and easy way. Get the details on the process, steps, and required documents. Check your registration status and make sure you’re on track to meet deadlines. Contact us today to learn more!

GSTIN stands for Goods and Services Tax Identification Number. It is a unique 15-digit number assigned to every taxpayer registered under the GST regime in India. The GSTIN is used to identify taxpayers and to track their transactions.
The GSTIN is structured as follows:
The Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) is a non-profit, non-government organisation that provides the shared IT infrastructure and services to the Central and State Governments, taxpayers and other stakeholders to implement the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India.
The GSTN is responsible for developing and maintaining the GST portal, which is the online platform that taxpayers use to register for GST, file returns, and make payments.
The GSTN also provides several other services, such as:
The GSTN is a critical component of the GST system in India. It provides the IT infrastructure and services that enable taxpayers to comply with the GST laws and the government to administer the GST system.
A GST certificate is a document issued by the Government of India to a taxpayer or entity that has registered under the GST system. It is proof of registration and authorises the taxpayer to collect GST from customers on behalf of the government.
The GST certificate contains the following information:
The components of Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India are:
This is levied by the central government on all intra-state and inter-state supplies of goods and services. The CGST rate is the same for all states and union territories.
This is levied by the state government on all intra-state supplies of goods and services. The SGST rate varies from state to state.
This is levied by the central government on all inter-state supplies of goods and services. The IGST rate is the sum of the CGST and SGST rates.
This is levied by the central government on all supplies of goods and services made within a union territory. The UTGST rate is the same as the SGST rate.
| Type of transaction | CGST | SGST | UTGST | IGST |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-state supply of goods and services | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A |
| Inter-state supply of goods and services | N/A | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| Supply of goods and services from a state to a union territory | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Supply of goods and services from a union territory to a state | N/A | Yes | N/A | N/A |
| Supply of goods and services within a union territory | Yes | N/A | Yes | N/A |
The objectives of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India are to:
GST is a single tax that replaces multiple indirect taxes levied by the central and state governments. This makes it easier for businesses to comply with tax laws and reduces the cost of doing business.
The cascading effect of taxes occurs when a tax is levied on a product or service that already includes other taxes. This can lead to higher prices for consumers. GST eliminates the cascading effect of taxes by allowing businesses to claim input tax credits on the taxes paid on their inputs.
GST is expected to boost economic growth and development in India by creating a single market for goods and services. This will make it easier for businesses to trade across state borders and will lead to lower prices for consumers.
GST is expected to increase tax revenue for the government by widening the tax base and reducing tax evasion. This will help the government to fund essential public services.
The objectives of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India are to:
GST is a single tax that replaces multiple indirect taxes levied by the central and state governments. This makes it easier for businesses to comply with tax laws and reduces the cost of doing business.
The cascading effect of taxes occurs when a tax is levied on a product or service that already includes other taxes. This can lead to higher prices for consumers. GST eliminates the cascading effect of taxes by allowing businesses to claim input tax credits on the taxes paid on their inputs.
GST is expected to boost economic growth and development in India by creating a single market for goods and services. This will make it easier for businesses to trade across state borders and will lead to lower prices for consumers.
GST is expected to increase tax revenue for the government by widening the tax base and reducing tax evasion. This will help the government to fund essential public services.
| Business type | Required documents |
|---|---|
| Individual | PAN card, Aadhaar card, bank account statement or cancelled cheque, passport-size photograph |
| Partnership | PAN card of the firm, partnership deed, Aadhaar cards of all partners, bank account statement or cancelled cheque, passport-size photograph of one partner |
| Company | PAN card of the company, company incorporation certificate, Memorandum and Articles of Association, Aadhaar card of the authorised signatory, bank account statement or cancelled cheque, passport-size photograph of the authorised signatory |
| Non-resident | PAN card of the non-resident, passport, Aadhaar card or any other proof of address, bank account statement or cancelled cheque, passport-size photograph |
To apply for a GST number online, you can follow these steps:
Getting a GST registration is a legal process that requires you to submit a lot of information about your business and scanned copies of certain documents. Vakilsearch offers a GST registration plan that can save you a lot of time and hassle. With our plan, a GST professional will help you with the entire process from start to finish.
ComplianceFrequency
| File GSTR-1 (Sales return) | Monthly |
| File GSTR-3B (Summary return) | Monthly |
| Pay GST liability | Monthly |
| File GSTR-2 (Purchase return) | Quarterly |
| File GSTR-4 (E-commerce return) | Quarterly |
| File GSTR-5 (Non-resident return) | Quarterly |
| File GSTR-6 (Input service distributor return) | Quarterly |
| File GSTR-7 (Tax credit return) | Quarterly |
| File GSTR-8 (E-commerce return for e-commerce aggregators) | Quarterly |
| File GSTR-9 (Annual return) | Annual |
| File GSTR-9C (Reconciliation statement) | Annual |
| Issue invoices and credit notes | As required |
| Maintain GST records | As required |
| File GST refunds | As required |
| Respond to GST notices | As required |
| E-invoicing (for businesses with a turnover of more than ₹20 crores) | Monthly |
| Electronic waybill (EWB) (for all inter-state and intra-state movement of goods worth more than ₹50,000) | As required |
There are two ways to check your GST registration status online:
| Status code | Description |
|---|---|
| 01 | Return filed successfully |
| 02 | Return pending for review |
| 03 | Return rejected |
| 04 | Refund processed |
| 05 | Refund rejected |
| 06 | Refund pending for review |
| 07 | Refund on hold |
| 08 | Refund cancelled |
| 09 | Refund reversed |
| 10 | Notice issued |
| 11 | Notice complied with |
| 12 | Notice pending for compliance |
Please note that the imprisonment penalty is typically imposed only in cases of willful evasion of GST, which is a serious offence.
The penalty for failure to register for GST can be waived if the business registers for GST within 30 days of the date on which it was required to register.
A taxable person under GST is any person who is registered under GST or required to be registered under GST. Any person who engages in economic activity including trade and commerce is treated as a taxable person.
Types of taxable persons under GST:
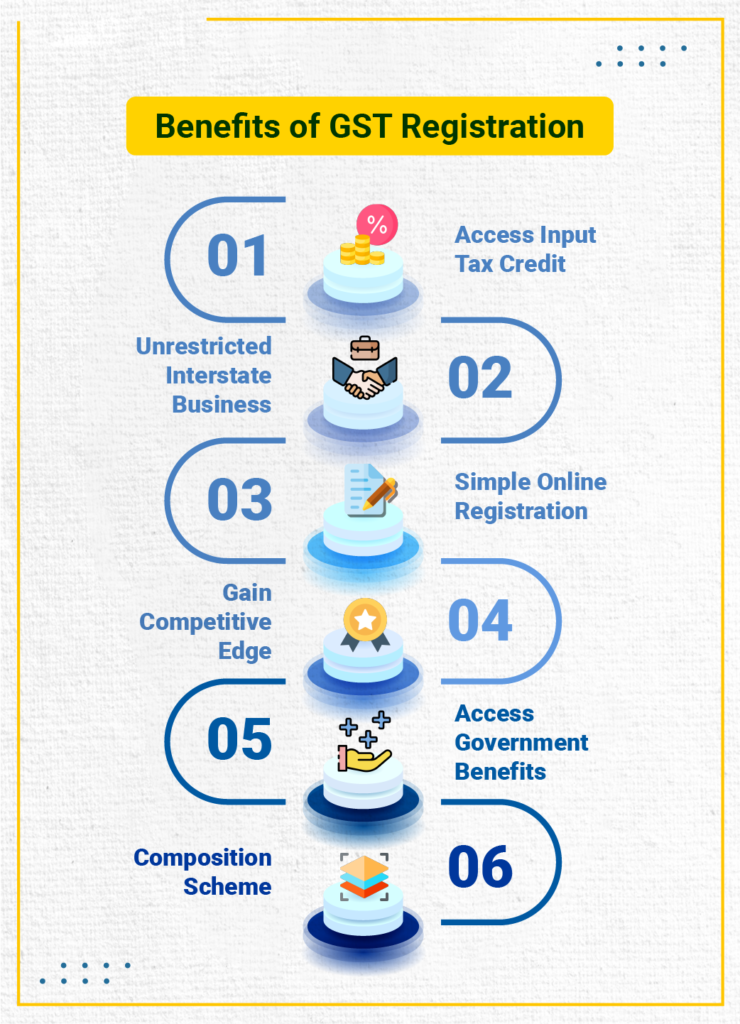
Voluntary registration under GST is registering for GST even if you are not required to do so by law. There are several benefits to voluntary registration, including:
| Goods and services | GST rate |
|---|---|
| Essential goods and services (e.g., food, beverages, educational services) | 5% |
| Most goods and services (e.g., clothing, electronics, household appliances) | 12% |
| Luxury goods and services (e.g., cars, jewellery, hotels) | 18% |
| Demerit goods and services (e.g., cigarettes, alcohol, gambling) | 28% |
GST return filing is the process of submitting GST returns to the government. GST returns are required to be filed by all businesses that are registered for GST. The frequency of GST return filing depends on the type of business and the turnover of the business.
